学习参考
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1085988
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38607035/article/details/82595032
目的:爬取PLAYERUNKNOWN’S BATTLEGROUNDS的评价
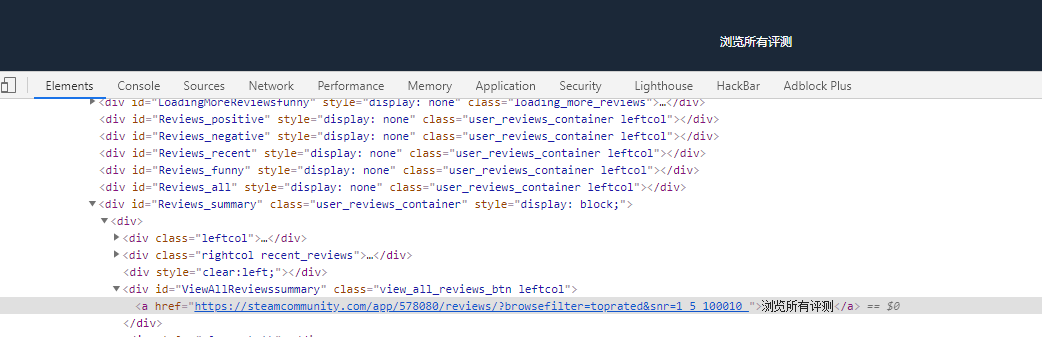 入口为:https://steamcommunity.com/app/578080/reviews/?browsefilter=toprated&snr=15_100010
入口为:https://steamcommunity.com/app/578080/reviews/?browsefilter=toprated&snr=15_100010
使用Chrome抓取网页请求。发现关键请求。

具体如下:
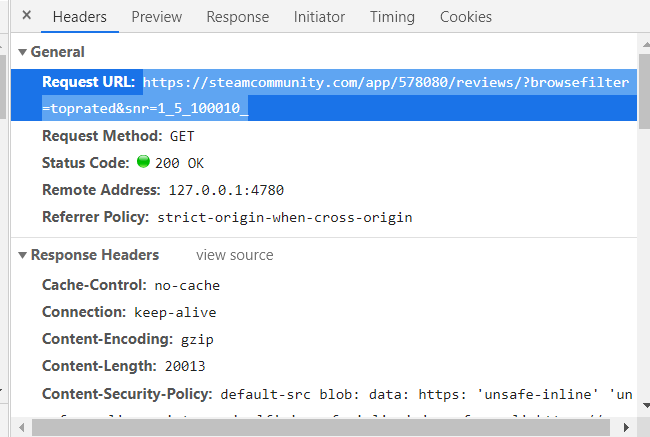
是个GET请求。
模拟请求,获得源码。
import requests
url = ‘https://steamcommunity.com/app/578080/reviews/?browsefilter=toprated&snr=1_5_100010_‘
html = requests.get(url).text
print(html)
UnicodeEncodeError: ‘gbk’ codec can’t encode character ‘\xa9’ in position 13282: illegal multibyte sequence
上网搜原因

检查网页源码,发现是zh-cn编码
import requests
import io
import sys
import urllib.request
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf8') #改变标准输出的默认编码
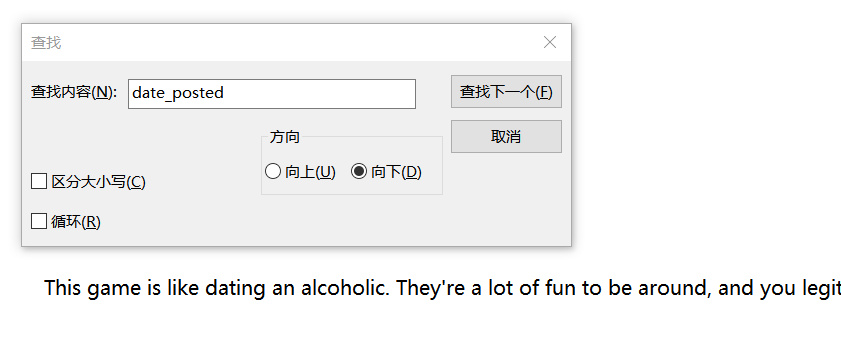
编译通过,通过审计代码发现可以显示英文评论,但是还是不能显示中文。(<div class="date_posted">)是通过检查出来的
接着查,改代码为
html = requests.get(url).read()
print(htmlBytes.decode('utf-8'))
好吧,,,还是不行
发现改个头就行
headers = { 'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.5,en;q=0.3'}
html = requests.get(url, headers=headers).text
print(type(html)) #测试得到html = requests.get(url).text是str格式,可以用soup解析。
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
用自带的解析器‘html.parser’也行。
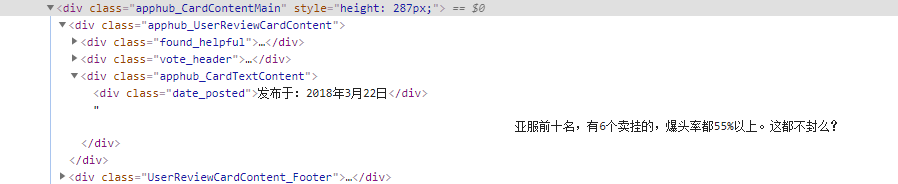
发现每个评论都在一个class=”apphub_CardContentMain”中 class=”date_posted”(包含日期和评论。
开始爬。
comments = soup.find_all('div', {'class': 'apphub_CardContentMain'})
for comment in comments:
print(comment.text)
结果如下: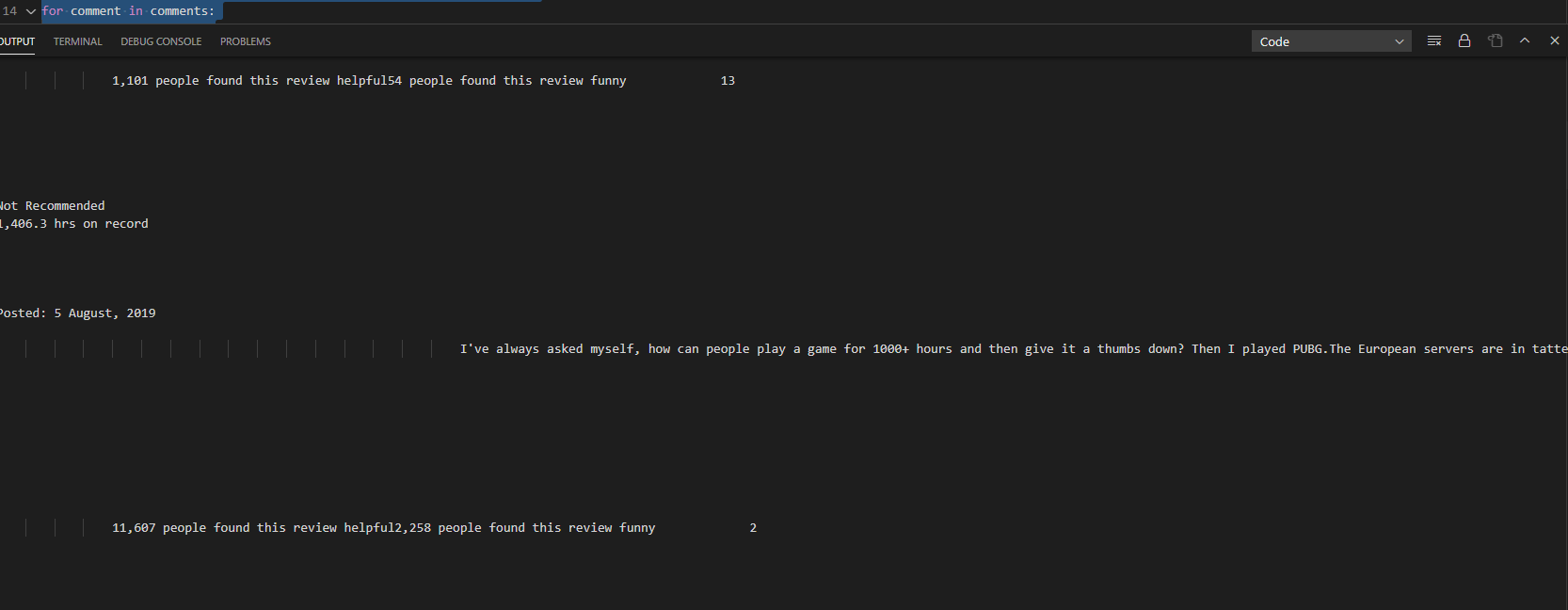
虽然爬出了评论和日期,但是空格过多。
用.strip()移除
抓包,加载新界面。
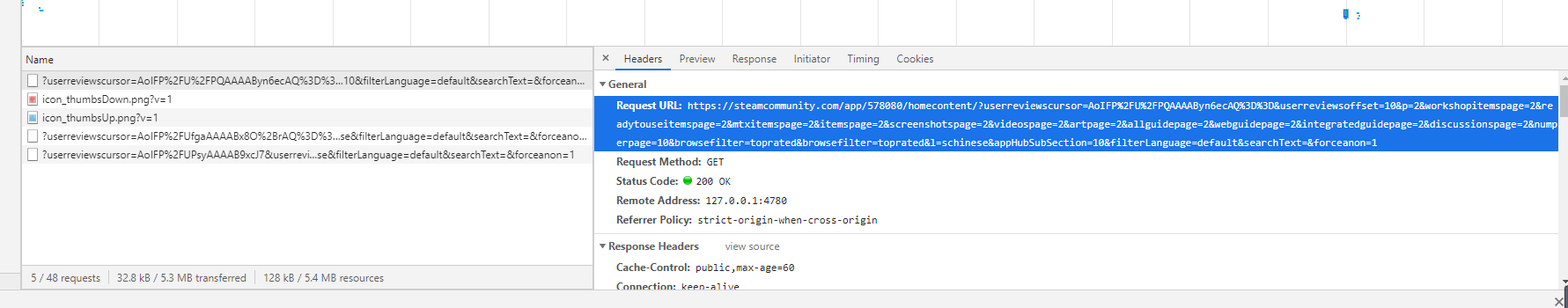

这些是控制新页面评论数的参数
这些是源url 注意参数上传方法。
https://steamcommunity.com/app/578080/homecontent/?userreviewscursor=AoIFP%2FU%2FPQAAAAByn6ecAQ%3D%3D&userreviewsoffset=10&p=2&workshopitemspage=2&readytouseitemspage=2&mtxitemspage=2&itemspage=2&screenshotspage=2&videospage=2&artpage=2&allguidepage=2&webguidepage=2&integratedguidepage=2&discussionspage=2&numperpage=10&browsefilter=toprated&browsefilter=toprated&l=schinese&appHubSubSection=10&filterLanguage=default&searchText=&forceanon=1
import requests
import io
import sys
import urllib.request
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf8') #改变标准输出的默认编码
headers = { 'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.5,en;q=0.3'}
for i in range(1,10):
url = 'https://steamcommunity.com/app/578080/homecontent/??userreviewsoffset=' + str(10 * (i - 1)) + '&p=' + str(i) + '&workshopitemspage=' + str(i) + '&readytouseitemspage=' + str(i) + '&mtxitemspage=' + str(i) + '&itemspage=' + str(i) + '&screenshotspage=' + str(i) + '&videospage=' + str(i) + '&artpage=' + str(i) + '&allguidepage=' + str(i) + '&webguidepage=' + str(i) + '&integratedguidepage=' + str(i) + '&discussionspage=' + str(i) + '&numperpage=10&browsefilter=toprated&browsefilter=toprated&appid=433850&appHubSubSection=10&l=schinese&filterLanguage=default&searchText=&forceanon=1'
html = requests.get(url, headers=headers).text
#print(type(html))
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
comments = soup.find_all('div', {'class': 'apphub_CardContentMain'})
for comment in comments:
print(comment.text.strip())
可以手动改爬多少条。此代码是100条。
改成存txt.
import requests
import io
import sys
import urllib.request
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf8') #改变标准输出的默认编码
headers = { 'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.5,en;q=0.3'}
file = open('steamComments.txt', 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
for i in range(1,10):
url = 'https://steamcommunity.com/app/578080/homecontent/??userreviewsoffset=' + str(10 * (i - 1)) + '&p=' + str(i) + '&workshopitemspage=' + str(i) + '&readytouseitemspage=' + str(i) + '&mtxitemspage=' + str(i) + '&itemspage=' + str(i) + '&screenshotspage=' + str(i) + '&videospage=' + str(i) + '&artpage=' + str(i) + '&allguidepage=' + str(i) + '&webguidepage=' + str(i) + '&integratedguidepage=' + str(i) + '&discussionspage=' + str(i) + '&numperpage=10&browsefilter=toprated&browsefilter=toprated&appid=433850&appHubSubSection=10&l=schinese&filterLanguage=default&searchText=&forceanon=1'
html = requests.get(url, headers=headers).text
#print(type(html))
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
comments = soup.find_all('div', {'class': 'apphub_CardContentMain'})
for comment in comments:
print(comment.text.strip())
file.write(comment.text.strip())
file.close
完成。
HTTP协议:全称是HyperText Transfer Protocol,中文意思是超文本传输协议,是一种发布和接收HTML页面的方法。服务器端口是80
HTTPS协议:是HTTP协议的加密版本,在HTTP的基础上加入了SSL层。服务器端口为443
注意:此过程关注点在Python爬虫并非细节请求过程
URL是Uniform Resource Locator的简写,统一资源定位符。 一个URL由以下几部分组成:
scheme://host:port/path/?query-string=xxx#anchor
http或者https以及ftp等。www.baidu.com。www.jianshu.com/trending/now,后面的trending/now就是path。www.baidu.com/s?wd=python,后面的wd=python就是查询字符串。在浏览器中请求一个url,浏览器会对这个url进行一个编码。除英文字母,数字和部分符号外,其他的全部使用百分号+十六进制码值进行编码。
在Http协议中,定义了八种请求方法。这里介绍两种常用的请求方法,分别是get请求和post请求。
get请求:一般情况下,只从服务器获取数据下来,并不会对服务器资源产生任何影响的时候会使用get请求。post请求:向服务器发送数据(登录)、上传文件等,会对服务器资源产生影响的时候会使用post请求。 以上是在网站开发中常用的两种方法。并且一般情况下都会遵循使用的原则。但是有的网站和服务器为了做反爬虫机制,也经常会不按常理出牌,有可能一个应该使用get方法的请求就一定要改成post请求,这个要视情况而定。在http协议中,向服务器发送一个请求,数据分为三部分,第一个是把数据放在url中,第二个是把数据放在body中(在post请求中),第三个就是把数据放在head中。这里介绍在网络爬虫中经常会用到的一些请求头参数:
User-Agent:浏览器名称。这个在网络爬虫中经常会被使用到。请求一个网页的时候,服务器通过这个参数就可以知道这个请求是由哪种浏览器发送的。如果我们是通过爬虫发送请求,那么我们的User-Agent就是Python,这对于那些有反爬虫机制的网站来说,可以轻易的判断你这个请求是爬虫。因此我们要经常设置这个值为一些浏览器的值,来伪装我们的爬虫。Referer:表明当前这个请求是从哪个url过来的。这个一般也可以用来做反爬虫技术。如果不是从指定页面过来的,那么就不做相关的响应。Cookie:http协议是无状态的。也就是同一个人发送了两次请求,服务器没有能力知道这两个请求是否来自同一个人。因此这时候就用cookie来做标识。一般如果想要做登录后才能访问的网站,那么就需要发送cookie信息了。200:请求正常,服务器正常的返回数据。301:永久重定向。比如在访问www.jingdong.com的时候会重定向到www.jd.com。302:临时重定向。比如在访问一个需要登录的页面的时候,而此时没有登录,那么就会重定向到登录页面。400:请求的url在服务器上找不到。换句话说就是请求url错误。403:服务器拒绝访问,权限不够。500:服务器内部错误。可能是服务器出现bug了。Chrome浏览器是一个非常亲近开发者的浏览器。可以方便的查看网络请求以及发送的参数。对着网页右键->检查。然后就可以打开开发者选项。打开Network(网络面板),刷新网页,点击加载的资源,可以在右侧资源查看相应 Header ,Preview,Response,Timing选项
# Beautiful Soup
pip install bs4
# 解析器
pip install lxml
pip install html5lib
# 初始化
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 方法一,直接打开文件
soup = BeautifulSoup(open("index.html"))
# 方法二,指定数据
resp = "<html>data</html>"
soup = BeautifulSoup(resp, 'lxml')
# soup 为 BeautifulSoup 类型对象
print(type(soup))
标签搜索有find_all() 和find() 两个基本的搜索方法,find_all() 方法会返回所有匹配关键字的标签列表,find()方法则只返回一个匹配结果。
1.已知ID link2_tag = soup.find(id='link2')
2.利用标签+class名(键值对)name_box = soup.find('h1', attrs={'class': 'name'})
# 指定 url
quote_page = 'http://www.bloomberg.com/quote/SPX:IND'
# 访问这个网站并且返回这个网站的 html 源码然后保存在 ‘page’ 中
page = urllib2.urlopen(quote_page)
# 使用 beautiful soup 解析这个 html 然后保存在 ‘soup’ 变量中。
soup = BeautifulSoup(page, 'html.parser')
# 获取 Class 对应的标签
name_box = soup.find('h1', attrs={'class': 'name'})
name = name_box.text.strip() # strip() 用来移除首尾的空白符
print name
soup = BeautifulSoup(resp, 'lxml')
# 返回一个标签名为"a"的Tag
soup.find("a")
# 返回所有tag 列表
soup.find_all("a")
## find_all方法可被简写
soup("a")
#找出所有以b开头的标签
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")):
print(tag.name)
#找出列表中的所有标签
soup.find_all(["a", "p"])
# 查找标签名为p,class属性为"title"
soup.find_all("p", "title")
# 查找属性id为"link2"
soup.find_all(id="link2")
# 查找存在属性id的
soup.find_all(id=True)
#
soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie"), id='link1')
#
soup.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"})
#查找标签文字包含"sisters"
soup.find(string=re.compile("sisters"))
# 获取指定数量的结果
soup.find_all("a", limit=2)
# 自定义匹配方法
def has_class_but_no_id(tag):
return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id')
soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id)
# 仅对属性使用自定义匹配方法
def not_lacie(href):
return href and not re.compile("lacie").search(href)
soup.find_all(href=not_lacie)
# 调用tag的 find_all() 方法时,Beautiful Soup会检索当前tag的所有子孙节点,如果只想搜索tag的直接子节点,可以使用参数 recursive=False
soup.find_all("title", recursive=False)
| find_parents() | 所有父辈节点 |
| find_parent() | 第一个父辈节点 |
| find_next_siblings() | 之后的所有兄弟节点 |
| find_next_sibling() | 之后的第一个兄弟节点 |
| find_previous_siblings() | 之前的所有兄弟节点 |
| find_previous_sibling() | 之前的第一个兄弟节点 |
| find_all_next() | 之后的所有元素 |
| find_next() | 之后的第一个元素 |
| find_all_previous() | 之前的所有元素 |
| find_previous() | 之前的第一个元素 |
Beautiful Soup支持大部分的CSS选择器 http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/selector.html, 在 Tag 或 BeautifulSoup 对象的 .select() 方法中传入字符串参数, 即可使用CSS选择器的语法找到tag。
html_doc = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc)
# 所有 a 标签
soup.select("a")
# 逐层查找
soup.select("body a")
soup.select("html head title")
# tag标签下的直接子标签
soup.select("head > title")
soup.select("p > #link1")
# 所有匹配标签之后的兄弟标签
soup.select("#link1 ~ .sister")
# 匹配标签之后的第一个兄弟标签
soup.select("#link1 + .sister")
# 根据calss类名
soup.select(".sister")
soup.select("[class~=sister]")
# 根据ID查找
soup.select("#link1")
soup.select("a#link1")
# 根据多个ID查找
soup.select("#link1,#link2")
# 根据属性查找
soup.select('a[href]')
# 根据属性值查找
soup.select('a[href^="http://example.com/"]')
soup.select('a[href$="tillie"]')
soup.select('a[href*=".com/el"]')
# 只获取一个匹配结果
soup.select(".sister", limit=1)
# 只获取一个匹配结果
soup.select_one(".sister")
soup = BeautifulSoup('<p class="body strikeout" id="1">Extremely bold</p><p class="body strikeout" id="2">Extremely bold2</p>')
# 获取所有的 p标签对象
tags = soup.find_all("p")
# 获取第一个p标签对象
tag = soup.p
# 输出标签类型
type(tag)
# 标签名
tag.name
# 标签属性
tag.attrs
# 标签属性class 的值
tag['class']
# 标签包含的文字内容,对象NavigableString 的内容
tag.string
# 返回标签内所有的文字内容
for string in tag.strings:
print(repr(string))
# 返回标签内所有的文字内容, 并去掉空行
for string in tag.stripped_strings:
print(repr(string))
# 获取到tag中包含的所有及包括子孙tag中的NavigableString内容,并以Unicode字符串格式输出
tag.get_text()
## 以"|"分隔
tag.get_text("|")
## 以"|"分隔,不输出空字符
tag.get_text("|", strip=True)
tag.contents # 返回第一层子节点的列表
tag.children # 返回第一层子节点的listiterator 对象
for child in tag.children:
print(child)
tag.descendants # 递归返回所有子节点
for child in tag.descendants:
print(child)
tag.parent # 返回第一层父节点标签
tag.parents # 递归得到元素的所有父辈节点
for parent in tag.parents:
if parent is None:
print(parent)
else:
print(parent.name)